Decoding the Future of Cardiology with Artificial Intelligence (AI)- New white paper available now
The DSPACE Innovation Hub at Daiichi Sankyo is proud to announce the publication of its first whitepaper “Heartbeats & Algorithms: “Decoding the Future of Cardiology with AI”.
The potential of AI to transform healthcare is a widely discussed topic, and at Daiichi Sankyo Belgium, our colleagues were keen to understand its implications for heart health. In the summer of 2024, they organized a think tank event in Brussels with leading cardiologists to discuss how AI can impact both healthcare providers and patients. The collective insights from this event were compiled into “Heartbeats & Algorithms”, a compelling whitepaper outlining the transformative potential of AI in cardiology. Curated by our experts from Belgium, Spain, Portugal and Germany, it is now available for download. Here’s a glimpse of its content:
Better heart health matters
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains the leading cause of death and disability in Europe, being responsible for approximately 10,000 deaths in the region every day.1 Despite decades of innovation leading to significant improvements in our ability to approach diagnosis and treatment of these diseases, the burden they inflict on patients, health systems, and society continues to rise.2
Simultaneously, digital technology – particularly AI – is advancing at record speed. The bracket term “Artificial Intelligence” encompasses a range of technologies that enable machines to mimic human intelligence, performing complex tasks once considered exclusive to humans:2
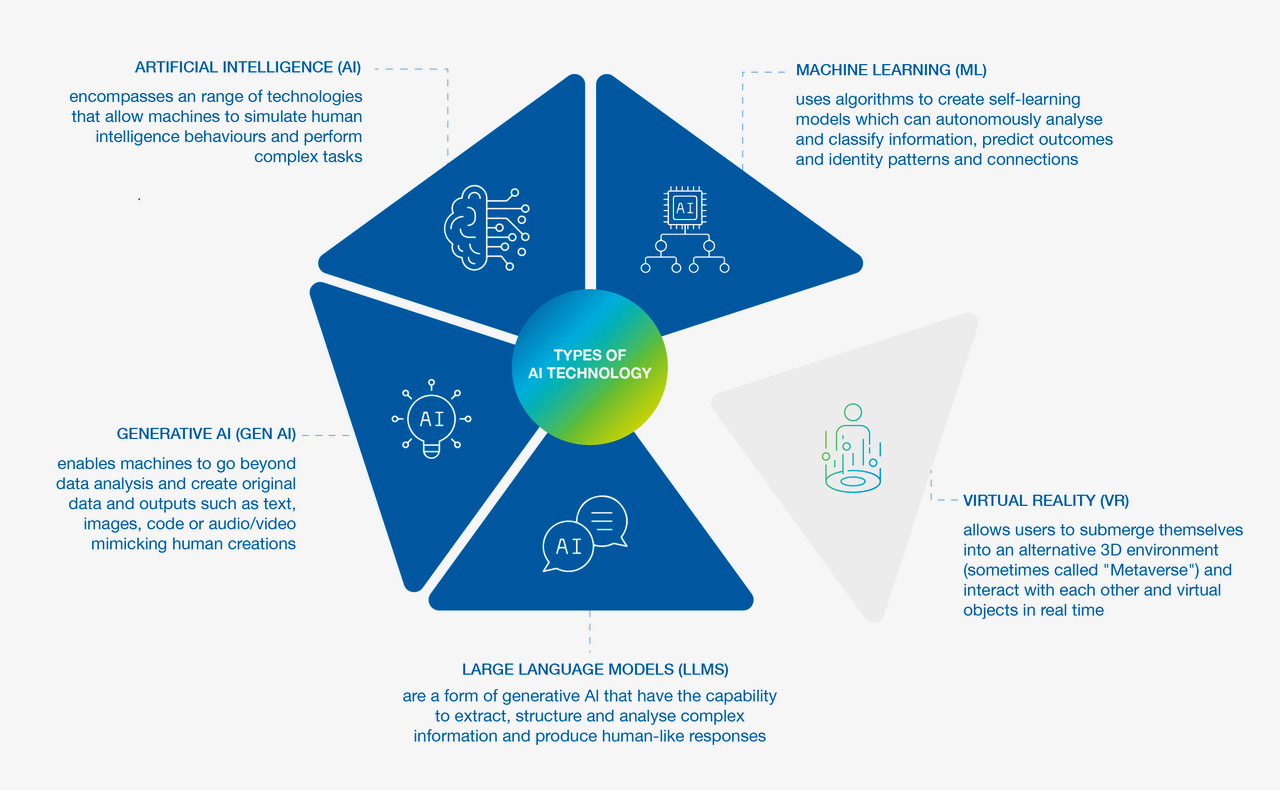
Opportunities for AI in Cardiology
During the think tank event, a strong focus for the cardiologists was on how AI can revolutionise CVD prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and control by leveraging new technology and vast data sources. The following five topics have been discussed intensively:
- AI as a means to alleviate administrative burdens: More time at the bedside
As the European population ages, the number of people living with CVD is increasing. This growing patient demand on cardiology services, workforce challenges, and the increasing complexity of care begs innovative solutions that AI might be able to provide. Smartly integrated, AI has the potential to minimize administrative tasks and create efficiencies that may allow cardiologists to see more patients, while improving the accuracy of patient’s records and the efficiency of follow-up care.3 - Optimized workflows: Better preparation, better treatment
AI-driven systems could automate the collection and summarisation of the required patient information ahead of the consultation. By analysing the medical history, condition, current treatments, and other clinical information, AI could enhance operational efficiency while supporting decision-making about treatment and care.3 - Enhanced diagnostics and personalized treatment: Take your diagnostics along for better care
A new generation of diagnostic tools provides solutions that are closer to the patient, outside of clinical settings. This includes point-of-care testing, wearable devices, and medical diagnostic software integrated into smartphones, e.g. to detect heartbeat irregularities. These tools enable real-time collection of physiological data from patients’ daily lives, indicating heart health status and informing easier and faster disease detection.4In the past, these devices have been useful to a certain extent but lacked the capability to match in-clinic diagnostic equipment when it comes to accuracy and reliability. However, with improvements in wearable technology and the incorporation of AI-enabled capabilities, these devices will continue to grow as powerful tools that enable patients to take control of their health on a day-to-day basis.
Personalised care involves customising medical care to the individual characteristics, needs, and preferences of each patient to improve treatment effectiveness and outcomes. AI technologies could make this feasible. Fed with a vast amount of patient data from a wide variety of sources, AI algorithms could lead to truly personalised treatment and care, integrating demographic data with patient-generated behavioural data and physiological data, imaging, and laboratory results.5
- Support for professional training: Upskilling our healthcare providers
Virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and high-fidelity bench simulations allow health-care professionals to test treatment strategies or enhance their technical expertise and surgical skills.6 AI-assisted extended reality (XR) technology may provide them access to a wide range of educational and simulated content, thereby expanding learning opportunities for scenarios typically inaccessible to many practitioners.7 - Improve patient empowerment: More support, better management
For patients to actively participate in the management of their condition, it is critical that they understand their diagnosis and its implications. The better equipped with knowledge they are, the more empowered patients can become.AI-powered virtual assistants or chatbots could offer patients clear, convenient, and accessible information about their condition and enable them to easily find health-related answers. This could include guidance on diet and lifestyle, medication information, adherence support, or practical help in managing the impact of symptoms on quality of life.8
AI-generated life-like avatars can further improve the experience by simulating human interactions more closely than text-based chatbots. The visual and auditory elements of a life-like avatar can capture and hold the attention of patients more effectively and the sense of personal connection might enhance trust and empathy.9
There are some challenges, too
While the potential benefits of AI in clinical care could be substantial, it is essential to address the associated risks through a careful and controlled integration process. The adoption of this technology should be backed by strong evidence demonstrating its capability, cost-effectiveness, superiority over existing technologies, and its impact on enhancing patient outcomes. It also needs to comply with the complex and developing legislation like the EU Artificial Intelligence Act.10
The cardiologists’ conclusions
AI is already transforming healthcare at a rapid pace, with systems and tools that are driving earlier and more accurate diagnoses, expediting and enhancing care delivery while improving patient outcomes.11
Achieving seamless integration of AI at its full potential in cardiology will require dedication, investment, innovation, and commitment to overcoming the many challenges involved.
It will require adaptation and harmonisation of systems and health infrastructure, integration of data and health records, and buy in from the entire health ecosystem, as well as continual improvement and honing of AI.
This can only be achieved through true collaboration and joint efforts between health and policy stakeholders, AI providers, industry partners and patients.
Download the Full Whitepaper
You can access the full whitepaper Heartbeats & Algorithms here.
Patients are central to everything we do at Daiichi Sankyo Europe. Our main purpose is to make a difference for patients with a holistic approach to care and treatment. At DSPACE, our digital innovation hub, our goal is to go beyond medicines. We deliver additional value by comprehensively understanding the needs of both patients and healthcare professionals, and providing digital add-on services to improve detection, diagnosis and treatment outcomes.